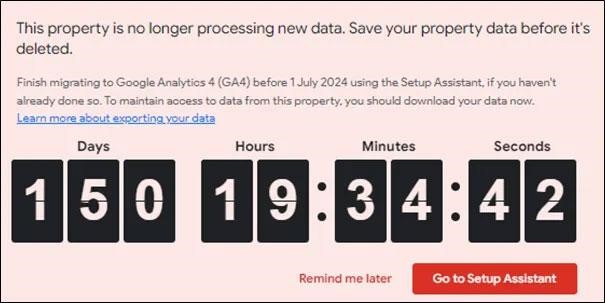
Google Analytics has been an indispensable tool for digital marketers, SEO experts, and business owners looking to understand visitor behavior and enhance the effectiveness of their websites. On July 1, 2023, Google officially replaced Google Analytics 3 (GA3), also known as Universal Analytics (GA-UA), with Google Analytics 4 (GA4)—a completely overhauled platform designed to offer more comprehensive and privacy-focused data handling. Although users have had access to their GA3 historical data within their Google Analytics dashboard, this will change with the planned removal of the GA3 data set for July 1, 2024.
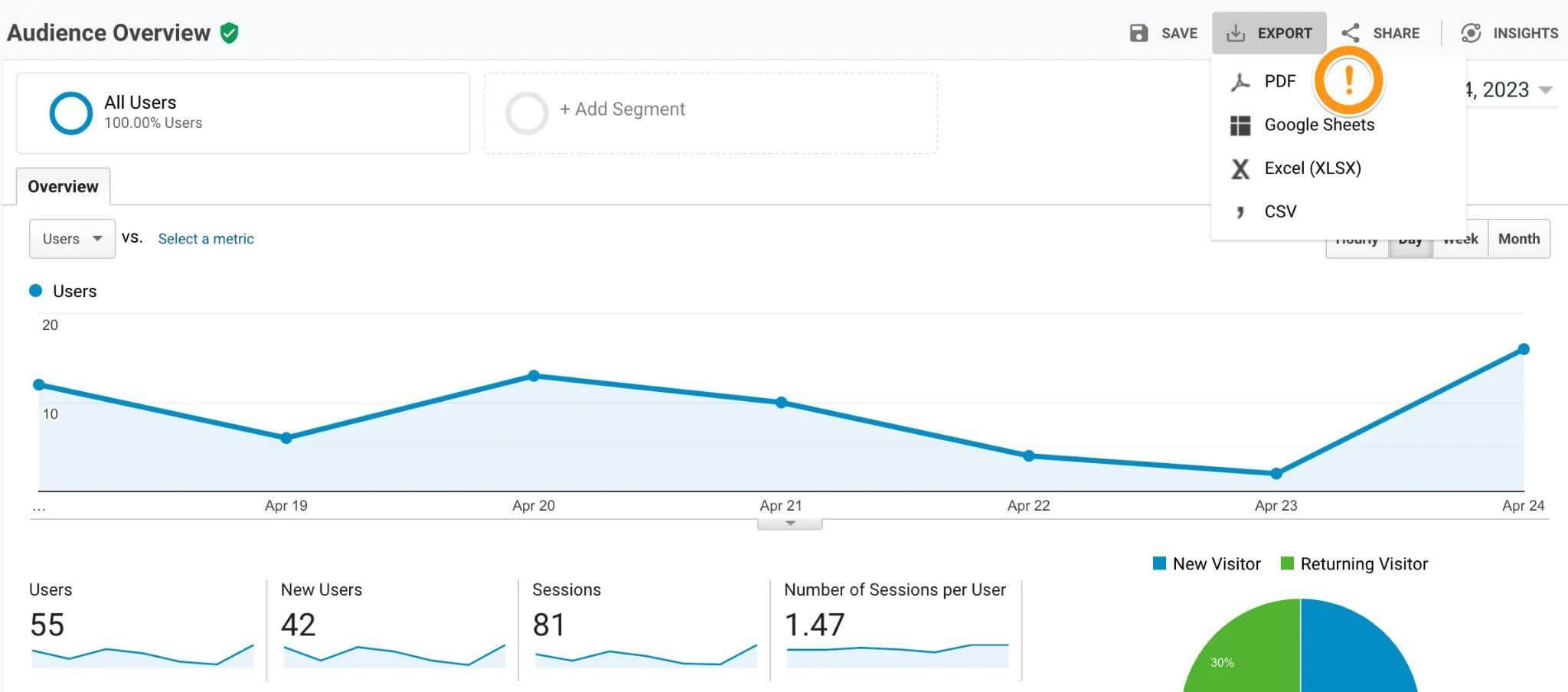
Quick Overview: Your GA3 Data Export
Many website owners will find that exporting their data into a simple CSV file might suffice for their needs. However, effectively managing and exporting analytics involves careful consideration of what data to export and the timeframes that are most relevant to business goals.
For those utilizing Google Analytics more extensively, the process can become complex very quickly. With approximately 70 different report types available and numerous potential timeframes for data collection, selecting the right datasets is crucial. For example, if GA3 was active from July 1, 2022, to July 1, 2023, and you needed month-over-month comparison reports along with a complete timeline report, you could be facing around 910 individual exports. This volume is typically impractical for most businesses, underscoring the importance of precisely identifying the necessary data and relevant periods to export.
Most users will find the investment unreasonable, so making informed choices about data exports is essential. This is where Ok Omni steps in. We can help ensure that your business—or your clients’ businesses, under a white-label—exports only the most valuable data.
If you are looking for a little support, get in touch with us today!
Migrate Data From GA3 to GA4
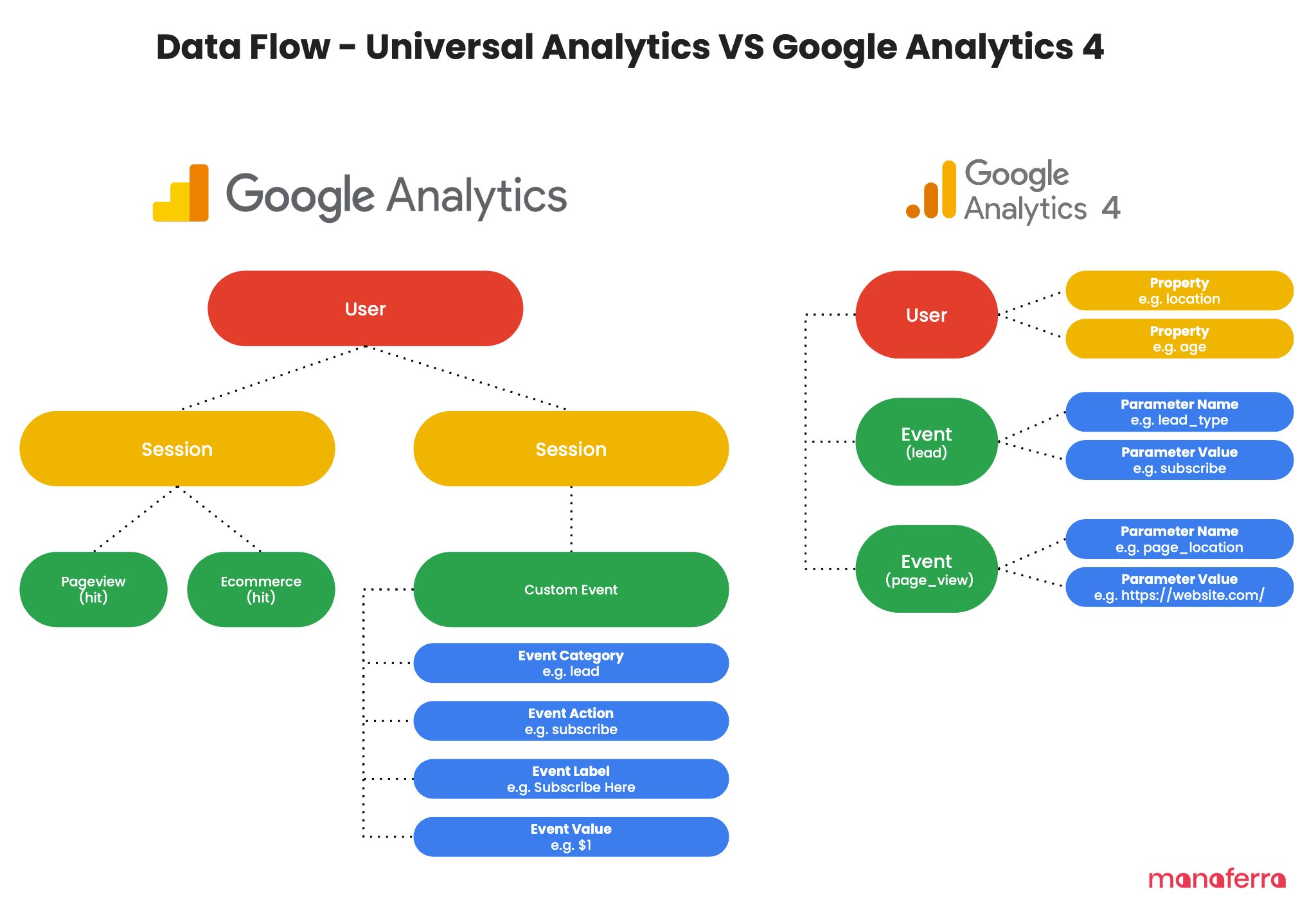
You may be thinking, “Where is the migrate from GA3 to GA4 button?”. The reality is that Google Analytics 3 and Google Analytics 4 operate on fundamentally different data models and architectures. This means they are not compatible “out of the box,” and transitioning from one to the other involves more than just a simple click.
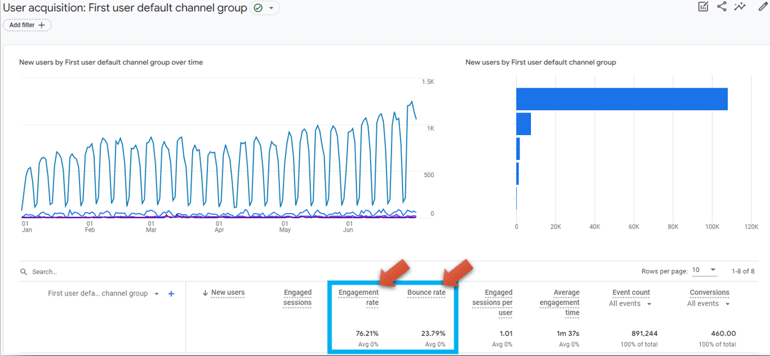
The Challenge of Incompatible Data Models
The migration process is beyond the scope of practical solutions for most website owners, especially small to mid-sized businesses, without extensive technical resources. For companies that do have the means to undertake such a transition, they still must grapple with reconciling the two different data models. This discrepancy can become apparent when comparing metrics across the two platforms. For example, during the switch from GA3 to GA4, many users noticed significant inconsistencies:
- Session Definitions: In GA3, sessions end after 30 minutes of inactivity or at midnight, creating distinct data segments for user activity. GA4, however, does not reset sessions at midnight and instead focuses on engagement duration and quality, leading to potentially lower session counts but possibly higher engagement metrics.
- User Tracking: GA3 uses a combination of cookies and user ID overviews to track new versus returning users, relying heavily on browser cookies. GA4 adopts a more flexible approach, utilizing a variety of user identifiers to track engagement across platforms and devices, which can alter user counts and engagement statistics.
- Metric Calculation: The bounce rate in GA3 simply reflects the percentage of single-page sessions without interactions. GA4 replaces this with an “engagement rate,” which considers sessions where the user was actively engaged on the site for over 10 seconds or interacted with the content. This shift aims to provide a more holistic view of user engagement but requires a different interpretive approach.
One key challenge with this transition is that data from GA3 cannot be directly imported into GA4 due to fundamental differences in how data is collected, processed, and reported. This means that the historical data valuable for year-over-year analysis and other longitudinal insights will no longer be accessible in the new system unless steps are taken to export and store it independently.
Detailed Guide to Exporting GA3 Data
The purpose of this blog post is to provide a practical guide for effectively exporting and storing GA3 data. We’ll explore the best methods for securing your historical data, ensuring that you can continue to leverage past analytics for future insights even after GA3 is completely removed. Whether you’re a seasoned analytics user or new to the platform, this guide will help you navigate the complexities of this transition smoothly and efficiently.
For those who recognize the importance of retaining their GA3 data, it’s essential to have a roadmap. Below are the steps you should take in your journey of exporting GA3 data.
- Addressing Data Quality
- Identify Essential Data
- Determine Relevant Timeframes
- Plan the Export Method
- Choose a Storage Solution
- Organize the Data Effectively
- Verify Data Integrity
Addressing Data Quality Concerns
Before committing to exporting large volumes of historical data, it’s essential to ask yourself “do I need this data?”. Assess the quality of the data you plan to keep. If your GA3 data has known issues—such as inaccuracies, duplications, or data pollution from poor tracking configurations—it may be wise to weigh the costs and benefits of exporting such data. In some cases, retaining flawed data can lead to misleading analysis and poor decision-making in the future.
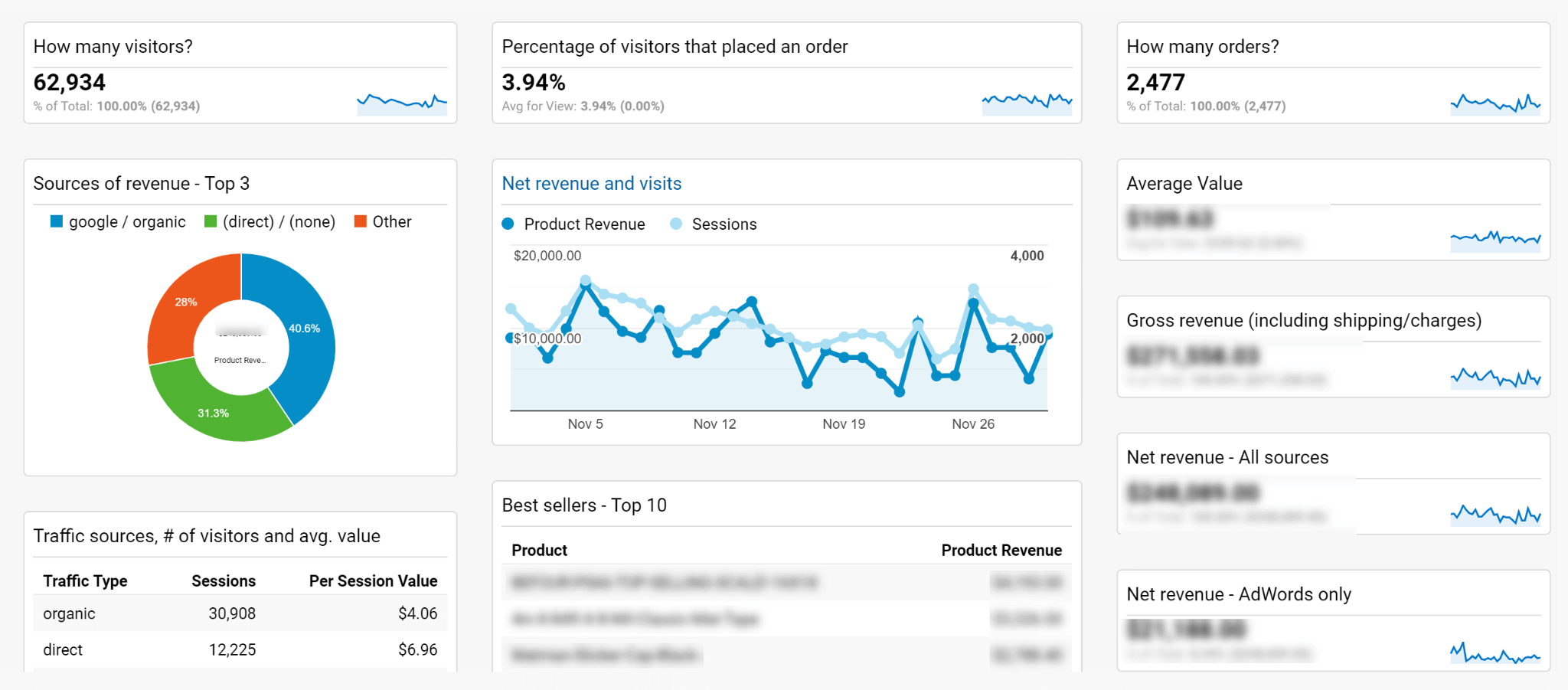
Consideration for Data Cleanup:
Evaluate Data Accuracy: Scrutinize your data for any signs of double tracking, tracking errors, or anomalies that could distort your analytics.
Impact of Bad Data: Understand that preserving and relying on incorrect data can compromise your insights and lead to strategic missteps.
Future-Focused Strategy: Sometimes, it might be more beneficial to focus on setting up GA4 with clean, accurate data rather than preserving a flawed historical record. Establishing a fresh and precise data environment in GA4 can provide a more reliable foundation for future analytics efforts.
Identify Essential Data
When planning your data export from GA3, it’s crucial to focus on the types of data that will provide the most value to your business moving forward.
There are:
- Audience [21]
- Acquisition [14]
- Behavior [18]
- Conversions [15]
In total, there are ~68 reports and subreports.
This estimation covers the standard reports available in most GA3 setups. Custom reports and segments that users may have created are not included in this count, as they can vary significantly between different Google Analytics installations.
What specific data from GA3 should be exported?
- Audience Reports
These reports provide insights into the characteristics of your website users, including demographics, interests, geolocation, behavior, technology, mobile usage, and more.
- Demographics (e.g., Age, Gender)
- Interests (e.g., Affinity Categories)
- Geo (e.g., Location, Language)
- Behavior (e.g., New vs Returning, Engagement)
- Technology (e.g., Browser & OS, Network)
- Mobile (e.g., Devices)
- Custom (e.g., Custom Variables, User Defined)
- Benchmarking (e.g., Channels, Location)
- Users Flow
- Acquisition Reports
These reports track how visitors arrive at your site and how different channels contribute to your traffic and conversions.
- All Traffic (e.g., Channels, Treemaps)
- Source/Medium
- Referrals
- Campaigns (including paid search)
- Keywords (both organic and paid)
- Social (e.g., Network Referrals, Landing Pages, Conversions)
- Cost Analysis
- Behavior Reports
These reports analyze what visitors do on your site, including the pages they visit and the actions they take.
- Behavior Flow
- Site Content (e.g., All Pages, Content Drilldown, Landing Pages, Exit Pages)
- Site Speed (e.g., Overview, Page Timings, Speed Suggestions)
- Site Search (e.g., Usage, Search Terms, Search Pages)
- Events (e.g., Top Events, Pages, Event Flow)
- AdSense (linked accounts)
- Experiments (A/B testing results)
- Conversion Reports
These reports focus on the goals and E-commerce activities on your site, tracking completions and measuring the economic performance.
- Goals (e.g., Overview, Goal URLs, Reverse Path, Funnel Visualization)
- E-commerce (e.g., Overview, Product Performance, Sales Performance, Transactions, Time to Purchase)
- Multi-Channel Funnels (e.g., Overview, Assisted Conversions, Top Conversion Paths, Path Length, Time Lag)
- Attribution (e.g., Model Comparison Tool)
Altogether, these main categories encapsulate numerous individual reports and sub-reports. Depending on how customized your Google Analytics setup is, you may have additional custom reports or modified versions of the standard reports.
Determine Relevant Timeframes
Deciding on the time periods for which you need to retain data is as crucial as identifying what data to keep. The timeframes you choose should provide the maximum strategic value for historical comparison and future planning. Here’s how to determine the most relevant time periods to focus on during your data export process.

What time periods do I need to retain GA3 data?
- Factors Influencing Timeframe Choices
Business Cycles: Consider your business’s seasonal trends and cycles. Retaining data that covers full business cycles, including peak seasons, holidays, and off-peak times, allows for accurate year-over-year comparisons and planning.
Duration of Data Utilization: Think about how long different types of data remain relevant to your business operations. For some metrics, such as campaign performance data, shorter time spans may be sufficient. For others, like audience growth and behavior trends, longer historical perspectives might be necessary.
Regulatory Requirements: Depending on your industry, there may be legal requirements dictating how long certain types of data need to be retained. Ensure compliance by including these regulatory timeframes in your data retention plans.
Key Business Events: Include data from periods surrounding major business events, such as product launches, market entries, or significant changes in strategy. This data is invaluable for assessing the impact of these events and guiding future initiatives.
- Recommended Timeframes
Last Three to Five Years: For most businesses, retaining data from the last three to five years provides a solid foundation for historical analysis. This range is typically long enough to observe and analyze long-term trends and patterns.
Year-Over-Year Comparisons: Ensure you have overlapping data for year-over-year comparisons. This means if you’re exporting data in 2023, you should include complete data sets from at least 2020 to 2023 to observe any cyclical trends or deviations from the norm.
Month-Over-Month and Week-Over-Week Data: For more detailed analysis, consider keeping detailed month-over-month or week-over-week data for the last 12 to 24 months. This granularity helps in pinpointing the onset of trends or shifts in user behavior.
- Implementing Your Timeframe Strategy
Create a Timeline Map: Map out a timeline of the selected timeframes, highlighting periods of particular interest or importance.
Use Custom Date Ranges in Exports: When setting up your data export from GA3, use custom date ranges to capture the specific periods identified. This helps in organizing the data for easy access and analysis in the future.
Document Rationale: Keep a record of why certain timeframes were chosen. This documentation can be helpful for future reference or for onboarding new team members.
Choosing the right timeframes for exporting data from GA3 is essential for maintaining a useful historical dataset that can inform future business strategies and provide valuable insights. By considering business cycles, regulatory requirements, and key business events, you can ensure that your data archive will serve as a robust resource for retrospective analysis and strategic planning.
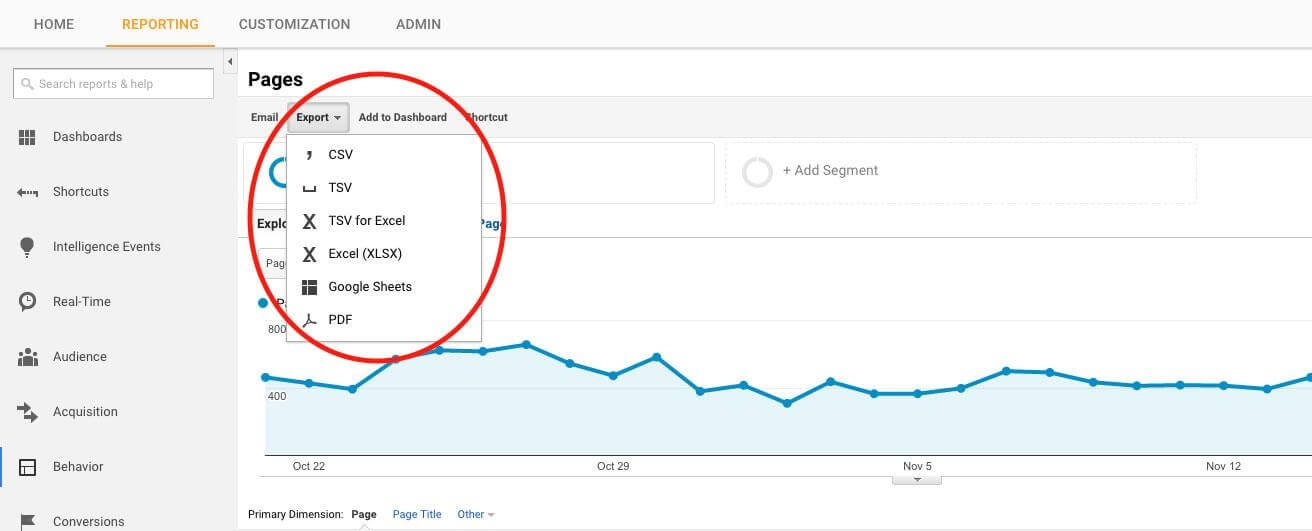
Plan the Export Method
When you’ve determined which data to export from Google Analytics 3 (GA3) and the timeframes that matter most, the next step is to establish how you will execute the export. This process involves selecting the right tools and understanding the steps needed to transfer your data effectively and securely.
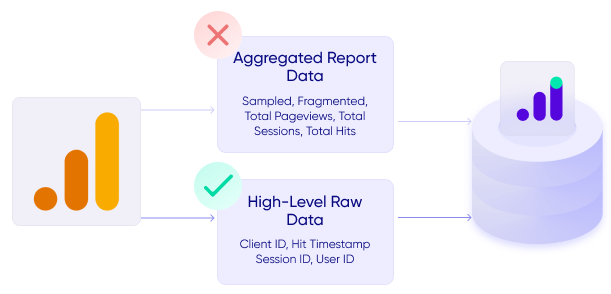
How will I export the data from GA3?
Exporting data from GA3 can be a complex process, especially when dealing with large datasets or customized reports. It’s important to use the right tools and procedures to ensure that data is exported accurately and efficiently.
Choosing the Right Tools
Google’s Native Export Features
Google Analytics Interface: GA3 offers native functionality to export reports directly from the interface. You can export data in various formats, such as CSV, Excel, and Google Sheets. This method is suitable for smaller data sets or when you need specific reports. This will fit the bill for most website owners and is the easiest to do.
Google Analytics API: For more comprehensive data needs, the Google Analytics API allows for more flexible and large-scale data exports. You can automate data exports using scripts, which is particularly useful for regularly updating your backups or integrating GA3 data with other business intelligence tools.
Third-Party Export Tools
Analytics Tools: Tools like Tableau, Looker, or Microsoft Power BI can connect directly to Google Analytics and help export data while also providing advanced visualization and analysis capabilities.
Data Integration Platforms: Platforms like Funnel, Supermetrics, or Stitch can automate data extraction from GA3 and integrate it with other data sources, simplifying the management of multi-source analytics environments.
BigQuery Integration
Direct Export From GA3 to BigQuery: For users with a Google Analytics 360 account, it’s possible to automatically export raw data from GA3 directly into BigQuery. This setup enables running complex queries against large datasets and integrating GA data with other business data effortlessly.
Benefits of Using BigQuery:
Scalability: BigQuery handles massive datasets with ease, making it suitable for enterprises or businesses with extensive data needs.
Speed: Provides fast SQL queries over large datasets, crucial for dynamic and complex analytical tasks.
Integration: Easily integrates with other Google Cloud services and third-party tools, supporting a comprehensive data ecosystem.
Advanced Analytics: Supports advanced analytical queries, including machine learning models directly within the data warehouse.
Choose a Storage Solution
Once you have established a method for exporting your data from Google Analytics 3 (GA3), the next critical step is to choose an appropriate storage solution. This decision will impact how you access, utilize, and secure your data in the long term. This section will guide you through evaluating different storage options, considering key factors like security, accessibility, and cost.
Considerations for Storage Options
When considering where to store your data, evaluate each option based on the following criteria:
Security: The chosen storage solution must provide robust security features to protect your data from unauthorized access and breaches. This includes physical security for hardware, as well as encryption and secure access protocols for digital storage.
Accessibility: Consider how easily you can access the data. If you need to integrate this data with other business systems or require frequent access for analysis, choose a solution that offers high availability and quick access times.
Cost: Storage costs can vary widely based on the amount of data, the required access speed, and the level of security. Assess the total cost of ownership, including initial investment and ongoing maintenance expenses.
Scalability: As your data needs grow, your storage solution should be able to scale accordingly. Whether you need more capacity or faster access, ensure that scaling is feasible and cost-effective with your chosen option.
In some instances, your data storage solution may already be predetermined, especially if you’re using services like BigQuery or various third-party tools. For example, many data integration companies handle the export and storage of your data on their servers, which you can access via a user-friendly web interface through their online portal. This approach simplifies the storage process considerably, but it also means you’re reliant on their services for as long as you need access to your data. It’s essential to thoroughly research and understand the terms, conditions, and dependencies involved before committing your data to such services. Always ensure that your business needs align with their offerings and consider the long-term implications of this partnership.
Storage Options
Cloud Storage Services
Examples: Google Cloud Storage, AWS S3, Microsoft Azure Storage, Google Drive
- Advantages:
- Scalability: Adapts easily to increasing data needs.
- Accessibility: Access data from anywhere, which is great for remote teams.
- Security: Includes features like encryption and multi-factor authentication.
- Considerations:
- Costs: Charges are based on storage volume and access frequency, which can add up.
- Connectivity: Dependence on a stable internet connection.
Google Drive Specifics
- Cost: The costs are relatively low compared to most other options.
- Integration: Seamless integration with Google Workspace tools.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy to use and manage, suitable for all levels of technical expertise.
Local Servers
- Advantages:
- Control: Full command over security and data management.
- Speed: Quick data access, ideal for large-scale analyses.
- Considerations:
- Initial Investment: High upfront costs for hardware and setup.
- Maintenance: Requires regular upkeep and security checks.
- Scalability: Additional hardware needed for expansion.
External Hard Drives
- Advantages:
- Portability: Easy to move and use in different locations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The initial expense is more affordable than other options.
- Considerations:
- Vulnerability: Risk of physical damage and data loss.
- Capacity: Not suitable for very large or growing data sets.
Choosing the right storage solution for your GA3 data is a pivotal decision that affects not just data security but also how effectively your organization can operate and analyze historical information. By carefully considering each option’s advantages and drawbacks, you can ensure that your data storage strategy supports your business’s needs both now and in the future.
Organize the Data Effectively
Once you’ve selected a storage solution and exported your GA3 data, the next crucial step is to organize this data effectively. Proper organization is key to ensuring that the data is not only secure but also readily accessible and easy to analyze. This section will guide you through planning a logical structure for storing your data, reflecting the organization used in GA3 and tailored to enhance usability and accessibility.
Effective data organization minimizes the time spent searching for specific datasets and maximizes the efficiency of analysis processes. It involves creating a systematic structure that aligns with how your business accesses and uses data, which can significantly impact productivity and analytical outcomes.

Principles of Effective Data Organization
Consistency: Maintain consistent naming conventions, file formats, and directory structures to reduce confusion and errors.
Accessibility: Organize data in a way that makes it easily accessible to authorized users, considering how frequently the data is accessed and by whom.
Security: This may fall under storage, but it is something to consider during the organization. Implement directory permissions and data access controls to protect sensitive information and comply with data privacy regulations.
Strategies for Organizing GA3 Data
Mirror GA3 Organization: Reflect the organizational structure of your GA3 account to minimize the learning curve and adaptation time for team members who are already familiar with the previous setup.
Categorization by Report Type: Group data into folders based on report types such as Audience, Acquisition, Behavior, and Conversions. This method aligns with how analytics data is typically reviewed and used in decision-making processes.
Example Report Type Structure:
- /GA3_Export
- /Audience
- /Acquisition
- /Behavior
- /Conversions
Sub-Categorization by Data Range or Business Function: Within each report type, files are further categorized by specific time ranges or by business functions to streamline access for users focused on particular aspects of the business.
Example Time Range Structure:
- /GA3_Export
- /Audience
- /2021
- /2022
- /Acquisition
- /2021
- /2022
- /Audience
Example Business Function Structure:
- /GA3_Export
- /Audience
- /Marketing
- /Sales
- /Acquisition
- /PPC_Campaigns
- /Organic_Search
- /Audience
Use Descriptive File Names: Include clear, descriptive names for files and folders, incorporating key details such as the report type, content, and time period covered. This helps quickly identify the right dataset needed for analysis.
Example File Naming:
user_demographics_2021.csv
Traffic_sources_jan-jun_2022.csv
Implementing Your Organization Plan
Set Up the Initial Structure: Based on the chosen categorization strategy, create the directory and folder structure on your chosen storage platform.
Document the Structure: Maintain detailed documentation of the data organization structure. This documentation should include a directory tree and descriptions of what each folder and file contains, which can be invaluable for onboarding new team members and ensuring continuity.
Organizing your exported GA3 data logically and systematically is crucial for maintaining efficiency in data access and analysis. By mirroring the GA3 structure, categorizing data thoughtfully, and using descriptive naming conventions, you can ensure that your valuable analytics data remains organized, secure, and ready for use whenever needed. This organization not only facilitates smoother operations but also enhances the overall analytical capability of your business.

Verify Data Integrity
After exporting your Google Analytics 3 (GA3) data and organizing it within your chosen storage solution, the final crucial step is to verify the integrity of the data. This process ensures that all necessary data has been successfully transferred, is accurate, and is usable in its new format. This section will guide you through developing a checklist and process to effectively verify the integrity of your exported data.
Data integrity verification is essential to confirm that the export process has not corrupted or altered the data in unintended ways. It involves checking that the data is complete, accurate, and remains consistent with its source in GA3.
Steps to Verify Data Integrity
Develop a Verification Checklist: Create a comprehensive checklist that includes all the datasets you’ve exported. Third-party vendors or platforms should have their own verification checks, but you should qualify for this yourself. The checklist should cover various aspects of data quality, including completeness, accuracy, and consistency.
- Data Completeness: Ensure no records are missing.
- Data Accuracy: Check that the data matches the source in GA3.
- Consistency: Verify that data formatting has remained consistent across all files.
- Conduct Spot Checks: Select random samples of your data to conduct detailed reviews. Compare these samples against the original data in GA3 to check for discrepancies or errors.
- Check for Data Corruption: Ensure that files have not been corrupted during the transfer process. This can be done by opening files and checking for any errors in opening or reading the data.
- Validate Against Known Metrics: Compare key metrics from the exported data with those reported in GA3 for the same periods. Significant discrepancies could indicate issues with the data export or transformation processes.
- Document the Validation Process: Keep a record of the validation process and any findings. This documentation is crucial for troubleshooting potential issues and for future audits of data integrity.
Verifying the integrity of your exported GA3 data is a critical step to ensure that your business can rely on this historical dataset for accurate insights and analysis. By systematically checking the completeness, accuracy, and consistency of your data and documenting the process, you safeguard the value of your data as a business asset.
Connect With Us at Ok Omni
Most users will find the investment of time in such extensive data backup unreasonable, but making informed choices about data exports is essential for maintaining access to valuable insights. This is where Ok Omni steps in. We specialize in helping businesses navigate their digital transitions smoothly, ensuring you export the data that offers the highest value. Whether you need assistance with simple exports or are looking for comprehensive backup solutions, Ok Omni is here to provide expert guidance and support. Contact us today.
To streamline your Google Analytics 3 export process, Ok Omni offers an all-inclusive analytics package designed to equip you with everything you need for a comprehensive insight into your web traffic and performance:
Professional Analytics Package – $300 (One-Time Fee)
Full PDF Report
Excel Data Export
BigQuery Export
Email Support
Includes 1 GA Property
Up to 10 downloads of different GA Views
Additional properties can be managed for $179 each.
Get Started
This package not only simplifies the process of deciphering what data should be exported, it also allows you to continue making insightful, data-driven decisions by covering a wide range of Google Analytics dimensions and metrics at monthly granularity covering most marketing analytics use-cases. Ready to optimize your data strategy?